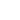In large-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, managing multiple strings of solar panels can quickly become a complex logistical challenge. This is where the DC Combiner plays a critical role. By consolidating numerous inputs into a single output, it simplifies the transition from the solar array to the inverter while providing essential protection.
Understanding the basics of wiring a DC Combiner is vital for ensuring system efficiency, safety, and compliance with electrical codes.
What is a DC Combiner Box?
A DC Combiner box acts as a central junction point. Its primary purpose is to take the direct current (DC) power generated by multiple solar strings and "combine" them into one main feed. This single output then carries the aggregated power to the central inverter.
Beyond simple cable management, the combiner box houses critical safety components like fuses, circuit breakers, and surge protection devices to prevent system damage from overcurrents or lightning strikes.
Core Components of the Wiring Interface
Before starting the wiring process, it is important to identify the internal architecture of the unit:
Input Terminals: These are the points where the individual positive and negative leads from each solar string enter the box.
Fuse Holders: Each positive string usually passes through a dedicated fuse to protect against reverse current flow.
Busbars: These are thick conductive metal bars (usually copper or aluminum) that collect the current from all the individual strings.
Main Disconnect Switch: This allows the operator to manually break the circuit for maintenance or in an emergency.
Surge Protective Device (SPD): This protects the sensitive electronics from voltage spikes.
Grounding Terminal: A dedicated point for the equipment grounding conductor.
Step-by-Step DC Combiner Wiring Process
1. Preparation and Cable Entry
Begin by ensuring all solar strings are disconnected or shaded to prevent live-wire hazards. Use liquid-tight conduits and cord grips (strain reliefs) at the entry points of the DC Combiner box. This prevents moisture ingress and ensures the cables do not pull on the internal terminals.
2. Wiring the Individual Strings
Each solar string consists of a positive and a negative cable.
Connect the positive leads to the individual fuse holders.
Connect the negative leads to the common negative busbar. It is essential to maintain consistent labeling for each string to make future troubleshooting much easier.
3. Connecting to the Main Busbars
Once the individual strings are fused, the current flows into the positive and negative busbars. Ensure that all terminal screws are tightened to the manufacturer's specified torque settings. Loose connections are a leading cause of electrical fires in DC systems due to high contact resistance and subsequent heat buildup.
4. Output Wiring to the Inverter
The output cables (the "home run" cables) are typically much thicker than the individual string wires because they carry the combined current of the entire array. These cables connect from the main output lugs of the DC Combiner to the DC input section of the inverter.
5. Grounding and Surge Protection
Connect the system ground to the grounding busbar. Ensure the Surge Protective Device is correctly wired to both the DC rails and the ground. This provides a safe path for excess energy to dissipate in the event of a surge.
Key Best Practices for a Reliable Installation
To ensure your DC Combiner performs optimally over the 25-year lifespan of a solar project, keep these tips in mind:
Verify Voltage Compatibility: Always ensure the combiner box is rated for the maximum open-circuit voltage (Voc) of your strings, commonly 600V, 1000V, or 1500V DC.Check Thermal Management: Ensure the box is mounted in a shaded area or has adequate ventilation. High temperatures inside the enclosure can lead to premature aging of the components.Wire Management: Use UV-rated cable ties to keep internal wiring neat. This prevents wires from resting against sharp edges or interfering with the door seal.Final Inspection: Before energizing, perform a continuity test and verify the polarity of every string. Reversing the polarity of even one string can cause significant damage.

Summary
Wiring a DC Combiner is a foundational skill in solar installation. By centralizing protection and streamlining the cabling process, you create a safer and more maintainable system. Always follow local electrical codes (such as the NEC in the US) and prioritize high-quality connections to ensure the long-term success of your PV array.

 简中
简中